Introduction
In modern organic chemistry, some reactions appear simple on the surface, but upon closer examination have deep industrial, scientific and practical significance. Aggregation and transformation pathways involving hcooch ch2 h2o often confuse students, researchers, and even professionals who want to understand how these molecules behave under different reaction conditions. Seriously, People often search for this , this particular query because it LEADS , LEADS to basic concepts related to hydrolysis, ester reactions, carbon bond behavior, and intermediate product formation.
Understanding these reactions not only provides a solid foundation for organic chemistry, but also opens the door to industrial applications including solvents, fuel additives, polymer production, and biochemical transformations. This article explores the chemistry behind the user query set with , with clarity, depth and a real-world approach. Guess what? No fluff and AI-style keyboard shortcuts—just clear explanations, long paragraphs, and well-organized tables and insights that help students fully understand the flow and significance of the interaction.
Table of Contents
What Does the Query “hcooch ch2 h2o” Actually Indicate?
When users enter the query hcooch ch2 h2o they are usually referring to a reaction involving methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) a CH₂ group environment and water (H₂O) that together raise questions about the mechanism of the reaction and its products. Methyl formate is an ester and esters , esters are known to undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water , water especially when heat or a catalyst is introduced. Guess what? The presence of “CH2” often reflects the user’s attempt to determine the behavior of the primary carbon or intermediate carbon , carbon group involved in the transformation process.
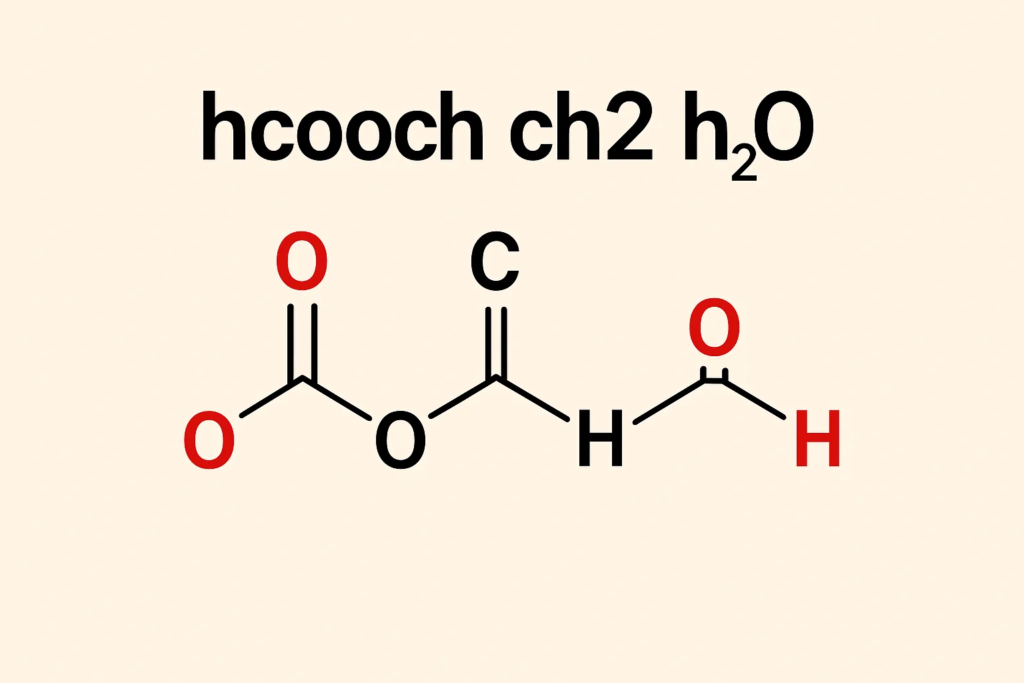
If interpreted correctly the query , query refers directly to the hydrolysis of methyl formate that breaks the ester bond and yields formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH₃OH) as major products. Like This crucial , crucial reaction forms the basis of a bunch of industrial processes and provides practical evidence for the stabilization of esters , esters nucleophilic attack by water and the formation of alcohols and carboxylic acids hotly debated , debated in advanced chemistry.
Understanding the Structure of hcooch ch2 h2o (Methyl Formate)
hcooch ch2 h2o commonly known as methyl formate is the simplest ester derived from formic acid. And oh yeah It consists of a –HCOO (formate) group linked to the –CH₃ group , group through an ester bond. Guess what? This , This single bond controls the behavior of the molecule especially during hydrolysis or reactions involving nucleophiles. Like A strong , strong hook for chemistry students is that this ester , ester is particularly reactive as formate esters tend to hydrolyze more quickly than a bunch of other carboxylic acid esters.
This property gives methyl formate , formate industrial importance in areas where rapid conversion is beneficial. And oh yeah Plus its relatively low boiling point and stability under mild conditions make , make it a suitable molecule for laboratories investigating fundamental reaction pathways. Understanding the reaction of methyl , methyl formate with water helps students explore broader concepts related to organic chemistry including carbonyl behavior resonance structures and the electrochemical properties of carbonyl carbons.
Molecular – Composition and Key Properties
| Property | HCOOCH₃ (Methyl Formate) |
| Molecular Formula | C₂H₄O₂ |
| Functional Group | Ester |
| Molar Mass | ~60.05 g/mol |
| Key Reaction | Hydrolysis (with water) |
| Main Products After Reaction | Formic acid + Methanol |
This table summarizes the core facts needed before diving into the chemical behavior of methyl formate in the presence of CH₂ environments and water.
What Role Does hcooch ch2 h2o Play in This Reaction Pathway?
The notation “hcooch ch2 h2o” in the user query can confuse , confuse beginners, since CH2 does not always refer to an independent molecule, but often to a methylene group… And oh yeah, In a bunch of mechanisms, CH2 can represent a reaction intermediate, a binding environment, or sometimes a simplification used to abbreviate organic structures. In the context of the hydrolysis of methyl formate, CH2 is not a separate reactant but part of the molecular framework that participates in bond rearrangement when the ester is broken. It helps us understand how carbon chains shift, how protons shift, and how new bonds , bonds form when an ester is attacked by water.
In a real chemical sense, CH₂ does not react on its own, but participates structurally and electronically when water attacks the carbonyl carbon of hcooch ch2 h2o₃, leading to decomposition. Recognizing this prevents misinterpretation and improves understanding of organic reaction pathways, especially for students preparing for exams , exams or researchers performing modeling simulations.
How H₂O (Water) Drives Hydrolysis in Ester Reactions
Water plays the main role in hydrolysis. Seriously Degradation of the ester , ester is impossible without water because , because the nucleophile needed to attack the carbonyl carbon is not present. When methyl formate comes into contact with water especially under acidic or basic conditions the water molecule attacks the carbonyl carbon atom breaking the ester , ester bond and producing an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
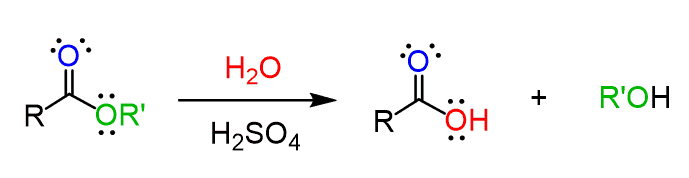
This mechanism is a feature of organic chemistry and is taught , taught in reaction classes but is often misunderstood because students bypass the logic of electron flow. Understanding how water donates electrons how carbonyls behave , behave and how proton transfers stabilize products makes , makes the overall , overall reaction clear. The presence of water transforms methyl formate from , from a stable ester into two chemically valuable and industrially viable molecules. Like Thus hydrolysis is more than a classroom concept – it becomes a practical tool in the chemical processing industry.
Mechanism – Step-by-Step Hydrolysis Pathway
| Step | Reaction Summary |
| 1 | Water attacks the carbonyl carbon of hcooch ch2 h2o |
| 2 | Formation of a tetrahedral intermediate |
| 3 | Proton transfers occur inside the intermediate |
| 4 | Ester bond breaks, forming formic acid and methanol |
| 5 | Final stabilization produces pure HCOOH + CH₃OH |
This table outlines the transformation mechanism without overcomplicating the electron-flow details.
Industrial Significance of the hcooch ch2 h2o Reaction
Industrially, the hydrolysis of methyl formate is not a simple laboratory demonstration. The reaction is widely , widely used in chemical synthesis, fuel production, bioplastic development, and some pharmaceutical processes. For example, formic acid—the main product—is widely used in leather processing, preservative formulations, textile treatment, and agricultural chemicals. Methanol, the byproduct, is essential in fuel blends, polymer synthesis, and the solvent industry.
The efficiency and predictability of the reaction allows manufacturers to economically produce these two compounds by controlling temperature, catalysts, and reaction time. In large plants, this transformation represents a cost-effective alternative to more complicated synthetic processes. And oh yeah, The reliability of the conversion makes it popular among chemical engineers who need high-throughput reactions. Like, When students understand these industrial applications, feedback becomes meaningful beyond theoretical study.
Real-World Problems This Reaction Helps Solve
Organic chemistry deals with countless reactions, but only a few of them help solve , solve real industrial, environmental, and laboratory problems, and this reaction is one of them. Hydrolysis of methyl formate contributes to sustainable processing as it can produce essential chemicals without , without causing serious pollution. In the environmental industry, formic acid is used as a biodegradable alternative to stronger acids.
The reaction also helps produce methanol used in clean fuels, that reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Guess what? In laboratories, the reaction is often used to teach , teach ester hydrolysis without hazardous chemicals, making , making it safer for students. Like, These real benefits highlight the importance of understanding the chemistry behind hcooch ch2 h2o behavior and interaction with water.
Conditions Required for Efficient Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis can occur under mild conditions, but the true conversion efficiency depends on temperature, presence of catalyst, and solvent conditions. And oh yeah, The ester bond in methyl formate is relatively reactive, but industrial processes still enhance the reaction by using acidic or basic catalysts. Acidic hydrolysis uses H⁺ ions to activate the carbonyl carbon, while , while basic hydrolysis results in a faster and sometimes irreversible transformation as it forms a carboxyl salt.
Like, Temperature also affects the speed of the reaction, moderate heat improves molecular collisions and ensures proper transformation. Without understanding these conditions, reaction yields may remain low. Knowing how to optimize these factors is essential for industries and laboratories involved in organic synthesis.
Important Reaction Conditions (Bullet Points Only Here)
- Moderate heating increases reaction speed significantly.
- Acidic catalysts create smoother, more controlled hydrolysis routes.
- Basic hydrolysis is faster but produces carboxylate salts instead of free acids.
- Excess water improves yield by pushing equilibrium toward hydrolysis.
- Proper stirring ensures uniform distribution and efficient molecular interaction.
Why Students Often Find This Reaction Confusing
a bunch of students hesitate when they see user queries like , like hcooch ch2 h2o because they assume its a complex multi-reactive chemical reaction… Seriously In fact the query refers to ester hydrolysis in structural context not three independent reactants. Students sometimes struggle because they are memorizing reactions rather , rather than electron mobility bond , bond strength intermediate formation and product stabilization.

Seriously Another reason is the inconsistency in the use of textbooks and websites that leads to misunderstandings about the existence of CH₂. Students also miss key conceptual clues that explain why water plays such , such a dominant role in breaking ester bonds. By making these little conceptual hurdles clear the reaction becomes , becomes easy to understand predictable and even , even fun.
Final Reaction Products and Their Uses
After the reaction is complete, two main products remain: formic acid (hcooch ch2 h2o) and methanol (hcooch ch2 h2o). These vehicles serve different industries and support a bunch of industrial sectors. Formic acid is critically important in textile finishing, rubber , rubber processing and antibacterial preparations.
Seriously, Methanol acts as an industrial solvent, a fuel mixture component, an antifreeze component, and a precursor to polymers such as formaldehyde resins. Understanding the products helps students understand why this , this reaction is so widely taught and often used in chemical manufacturing.
Conclusion
The query “hcooch ch2 h2o” may seem confusing at first glance but a deeper understanding reveals a simple , simple but very important chemical transformation. By exploring the structure of methyl formate the role of CH₂ in the molecular framework and the nucleophilic role , role of water we get a complete picture of ester hydrolysis and the valuable products it produces.
And oh yeah This reaction is not only essential in academic chemistry but also plays an important role in industrial synthesis environmental chemistry and manufacturing processes requiring formic acid and methanol. Understanding this reaction allows students and practitioners to confidently interpret organic reaction behavior. With , With the right conceptual foundation and real-world context what appears to be a fundamental question becomes an opportunity to understand a poignant chemical process.
FAQs
1. What is the main reaction that occurs between hcooch ch2 h2o?
This is an ester hydrolysis reaction that produces formic acid and methanol.
2. Does CH₂ act as a separate reactant in this reaction?
No CH2 represents a structural carbon group not an independent reactant.
3. Why does methyl formate , formate decompose easily?
You know what? Because the formate-ester bond is reactive and water easily attacks its carbonyl group.
You know , know what? 4. Are catalysts necessary for this , this REACTION?
NOT always but acidic or basic catalysts greatly increase the reaction rate.
5. And oh yeah What industries use the products of this reaction?
The textile fuel plastics pharmaceutical agricultural and chemical industries use formic , formic acid and methanol.
Also Read This: Best Blazertje Style Guide
